Electric Motors
Electric motors are fundamental components in a wide range of applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, providing efficient and reliable power for various devices and systems.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electric Motors
Electric motors operate based on the principles of electromagnetism. When an electric current passes through a wire in a magnetic field, it creates a force that causes the wire to move. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how electric motors work:
- Stator and Rotor: An electric motor consists of a stationary part called the stator and a rotating part called the rotor.
- Magnetic Field: The stator generates a magnetic field either through permanent magnets or electromagnets.
- Electric Current: An electric current flows through the windings of the rotor, creating its own magnetic field.
- Interaction: The interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and rotor generates a force that causes the rotor to spin.
- Rotation: This rotation converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, which can then be used to drive various mechanical components.
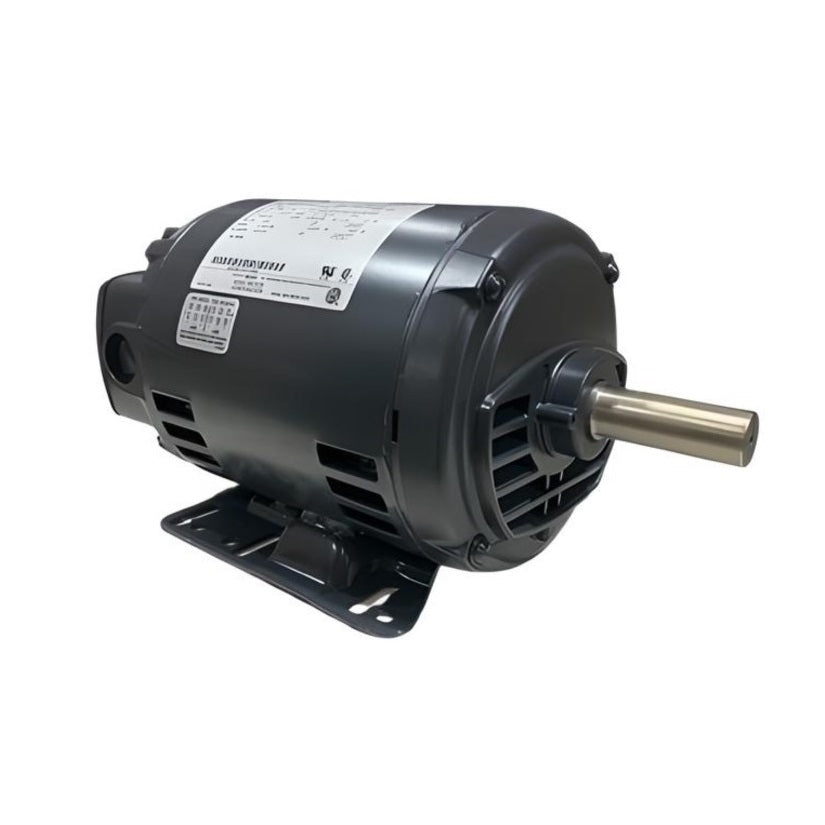
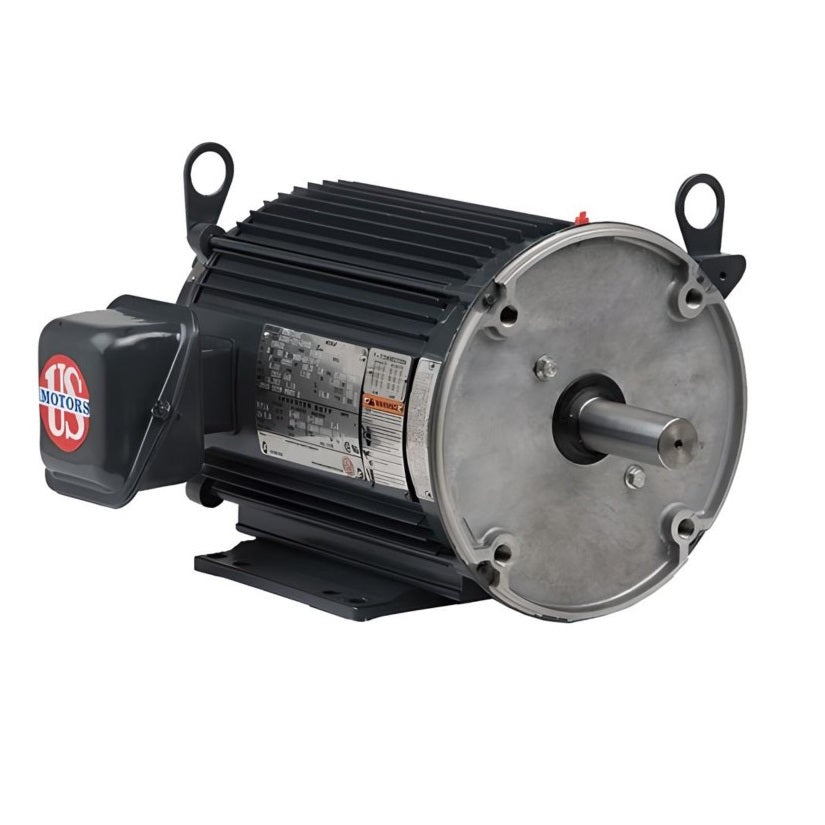
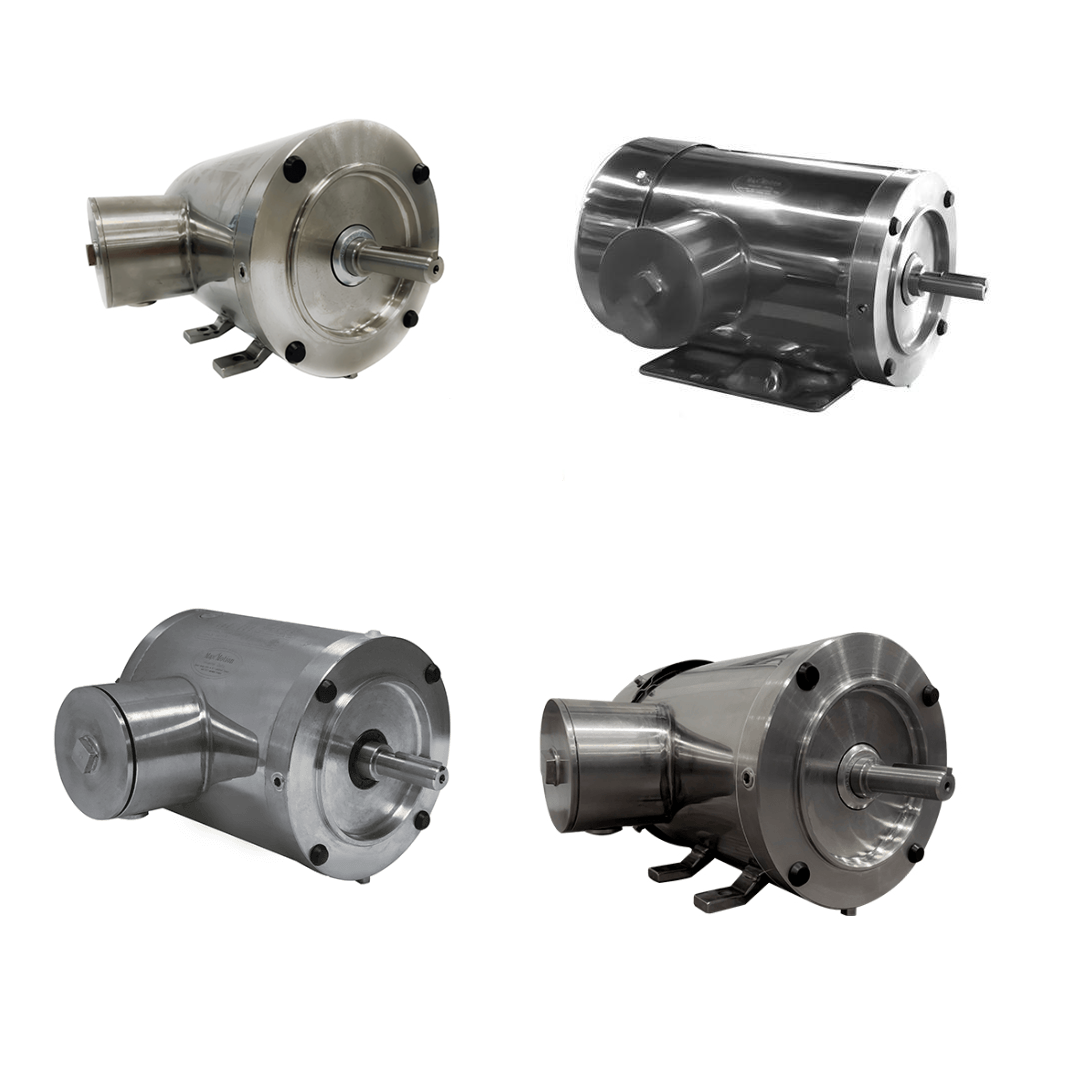
Electric motors are highly versatile and come in various types, including General Purpose Motors, IEC Metric Motors, Washdown Motors, Pump Motors and DC Motors , each suited for different applications.
Electric motors are used in a vast array of applications due to their efficiency and versatility. Some common uses include:
- Industrial Machinery: Electric motors power conveyors, pumps, fans, and compressors in manufacturing and processing plants.
- Household Appliances: They are integral to the operation of washing machines, refrigerators, vacuum cleaners, and air conditioners.
- Robotics: Electric motors provide precise control and movement in robotic arms and automation systems.
- HVAC Systems: They drive fans, blowers, and compressors in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Their ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy efficiently makes electric motors a cornerstone of modern technology.
Electric motors are known for their high efficiency compared to other types of motors. The efficiency of an electric motor is the ratio of mechanical power output to the electrical power input. Here are some key points about their efficiency:
- High Efficiency: Modern electric motors can achieve efficiency levels of over 90%, meaning they convert more than 90% of the electrical energy into useful mechanical energy.
- Low Energy Loss: Electric motors have minimal energy loss due to friction and heat, especially when compared to internal combustion engines.
- Variable Speed Control: Advanced motor controllers allow for precise speed and torque control, further optimizing efficiency.
- Energy Savings: High-efficiency electric motors contribute to significant energy savings, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Choosing high-efficiency electric motors can lead to substantial cost savings over time and support sustainability initiatives by reducing energy consumption.