FAQ
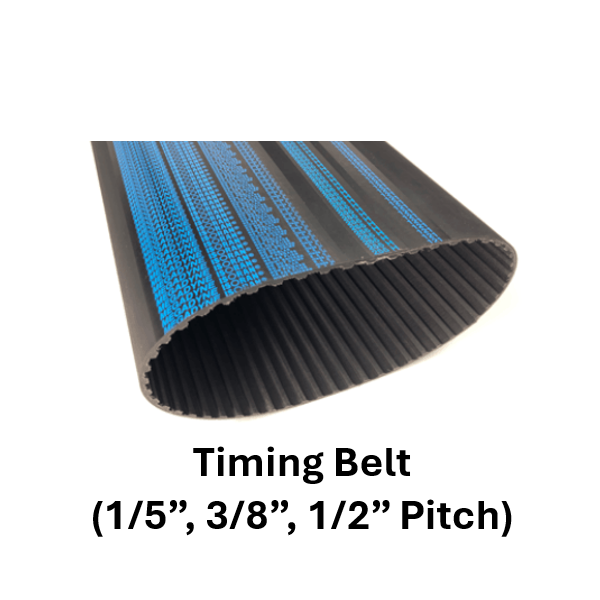
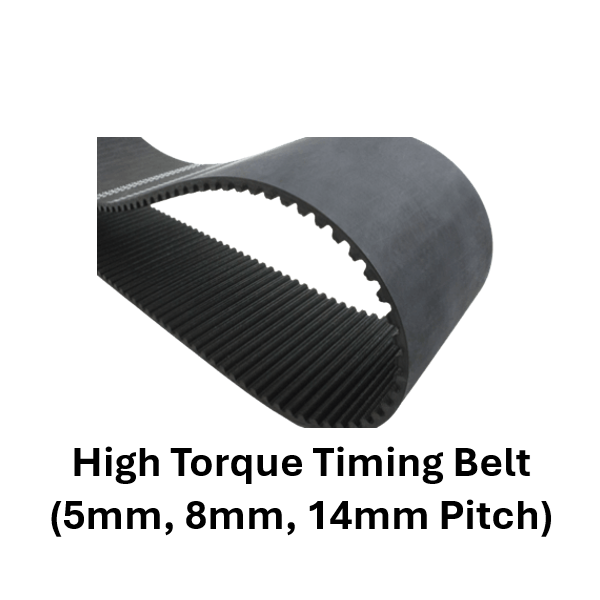
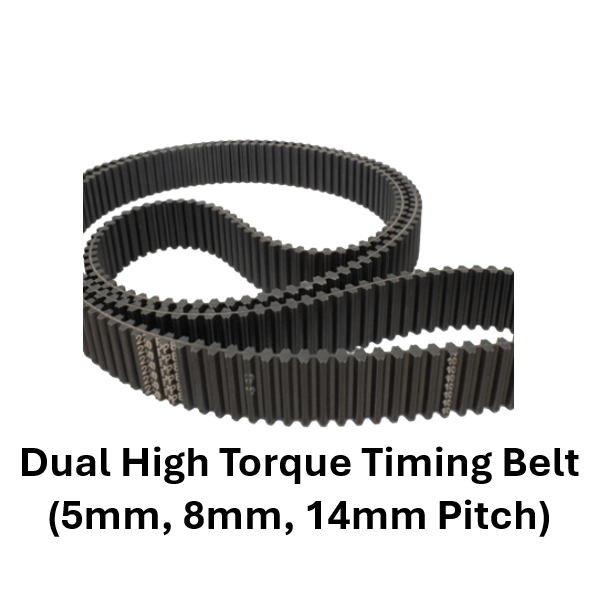
Timing belts are toothed belts made from durable materials such as rubber, polyurethane, or neoprene, reinforced with fibers like fiberglass or Kevlar. These belts are designed to synchronize the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft in internal combustion engines or to transfer motion and power in various mechanical systems. The teeth on the timing belt engage with corresponding grooves on pulleys, ensuring precise timing and efficient power transmission.
Timing belts are used in a wide range of applications across multiple industries. Common uses include:Industrial Machinery: Used in conveyor systems, packaging machines, and other equipment requiring precise and synchronized motion.
- Robotics: Employed in robotic arms and automated systems to provide accurate and reliable movement.
- Medical Equipment: Found in devices requiring precise and smooth operation, such as imaging machines and diagnostic equipment.
Their ability to provide accurate timing and efficient power transfer makes timing belts essential in many mechanical systems.
Timing belts work by transferring rotational motion and power between two or more shafts in a synchronized manner. Here’s how they function:
- Engagement: The teeth on the timing belt mesh with the corresponding grooves on the pulleys, ensuring a secure and precise fit.
- Rotation: As the driving pulley rotates, it moves the timing belt, which in turn rotates the driven pulley(s).
- Synchronization: The engagement of the teeth ensures that the rotation of the pulleys is perfectly synchronized, maintaining precise timing between the connected components.
- Tension: Proper tension is maintained in the belt to prevent slippage and ensure efficient power transmission.
This mechanism allows timing belts to deliver reliable and precise motion control in various applications.
Timing belts are manufactured using high-quality materials and advanced production techniques to ensure durability, precision, and performance. The typical manufacturing process involves:
- Material Selection: High-quality rubber, polyurethane, or neoprene is selected for the belt, reinforced with strong fibers like fiberglass or Kevlar.
- Molding: The selected materials are molded into the desired belt shape, with precise teeth patterns formed on the surface.
- Curing: The molded belts undergo a curing process to enhance their strength and elasticity.
- Finishing: The belts are trimmed and finished to ensure accurate dimensions and smooth surfaces.
- Quality Control: Each timing belt undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to ensure it meets industry standards for performance, durability, and reliability.
This meticulous manufacturing process ensures that our timing belts provide optimal performance and longevity in demanding applications.